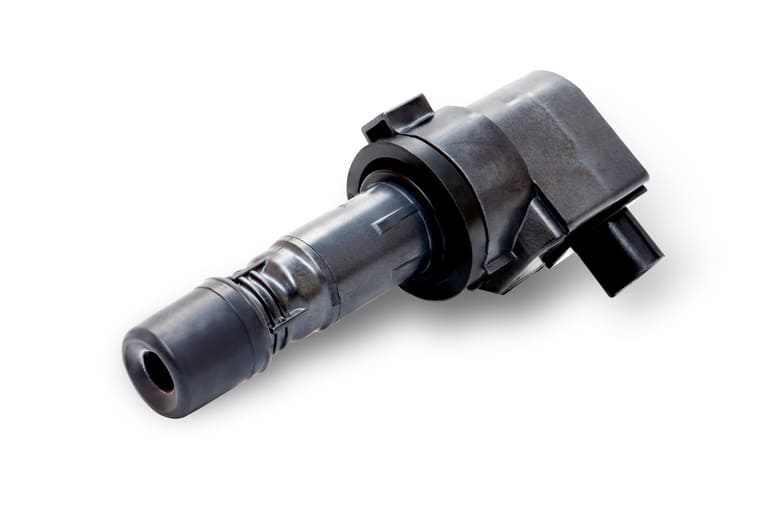

With broken ignition coils, your car won’t be going anywhere. Check out our guide to keep your car on the road.
As parts of the ignition system go, ignition coils are by far the most important. Without an ignition coil, the whole ignition system wouldn’t work. But it seems like spark plugs seem to get all the credit for this. People know how to and regularly do change their spark plugs and spark plug brands like Champion and NGK regularly sponsor everything from F1 to rally, but when it comes to ignition coils people don’t know exactly how they work or what they do.
The truth is though, that ignition coils are vital to the ignition system and can cause some serious problems if they go wrong. They could also be behind some of the common ignition problems that drivers experience on a daily basis.
Read on for our comprehensive guide to what ignition coils are, what they do, and how to spot when your coils are not working as they should.
What are ignition coils?
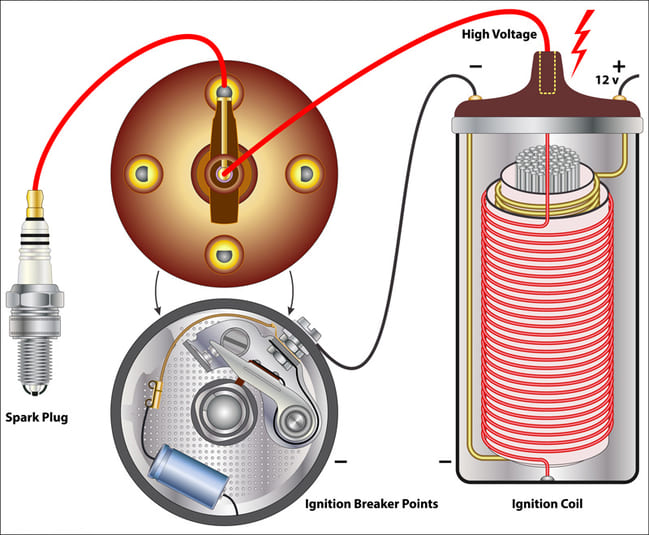
The ignition coils’ purpose is to amplify voltage from the battery so that a spark plug can ignite the engine’s air-fuel mixture. A fully charged car battery has a voltage of around 12.6V, but several thousand are needed to produce the spark that jumps the gap.
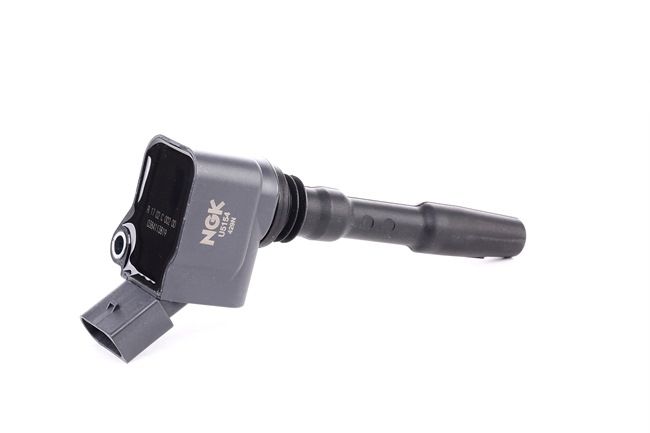
An ignition coil is normally two sets of coils, a primary and secondary, around an iron core and in a metal casing. This is then linked to the distributor and then the spark plugs. The output (called low-tension current) comes from the battery and is transformed by the coil into as much as 45,000 volts (called high-tension current) before getting to the spark plugs.
Some ignition systems will use one coil to provide the spark for all of the cylinders, however most newer designs use an individual coil for each cylinder.
In older cars, these will look like a small metal cylinder with wires sprouting out of it, one connecting it to the battery, another to the distributor.
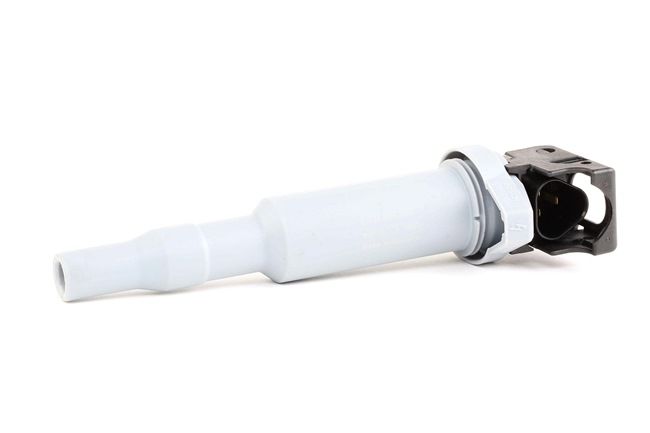
In modern cars, coils can be all shapes and sizes, including a single coil that looks like a long plastic tube – also known as a pencil or plug-shaft coil – one that incorporates an ignition module and another that looks like a plug you might find in your house.
You can also find coils that are laid out in a series and called cassette or sequence coils, or coil rails.

How do ignition coils work?
An ignition coil is essentially a small ‘step-up’ transformer. It relies on electromagnetism and to induce a high voltage from a low voltage. The primary winding has relatively few turns of heavy copper wire and the secondary winding has thousands of turns of very thin copper wire. Both windings are wound around each other.
The primary winding is connected to battery voltage and its earth can be switched on and off by the engine control unit (ECU). The secondary winding is connected to the spark plug. When the current is switched on, the primary wire receives the low voltage from the battery and generates a magnetic field around it.
However, the instant that flow is interrupted by the distributor, or in more modern ignition systems, the electronic control unit (ECU), the magnetic field collapses, creating or inducing a higher voltage in the secondary wire that travels to the spark plug. The magnetic iron core allows the electrical energy to pass between the two coils.
What problems can there be?
Given the ignition coils’ location right above the engines, meaning that they have to bear the brunt of the very hot combustion process in what is already a very warm engine bay. An ignition coil getting hot is always going to happen, but normally it doesn’t cause too much of a problem. For sensitive pieces of equipment like copper wiring, this is challenging.
In the process of induction, the coils get alternately hot and cold and are subjected to strong vibrations from the engine. This can cause the coils’ winding to break up over time, as well as cracks to the insulation and housing.
The main reason for ignition coils failure, though, is thanks to a voltage overload. This happens when spark plugs have been worn down and the electrode gaps are outside the specified limits or by damaged cabling and wires.
In time, the coil’s output voltage can rise to damaging levels, causing short circuits when it burns through the insulation. An ignition coil’s life expectancy is around 100,000 miles so it should be some time before it gives you trouble.
What are symptoms of ignition coil problems?
The symptoms are much those associated with components of the ignition system. It is important to note that any of these alone does not signal that there is a problem with the ignition coil, so it is important to check all parts of the ignition system to work out if it is the cause.
1. Misfiring engine, reduced power, and rough idle
Ignition coils going bad is almost certain to result in performance issues for the engine. Since the high voltage is needed for the spark plug to ignite the fuel-air mixture, if this isn’t there then the car will not start properly or the engine can misfire when driving along. This can also mean that the car doesn’t accelerate as it should do or there is a loss of overall power, because the fuel is not being ignited. It is also going to lead to a reduced fuel economy too.
2. Check Engine light comes on
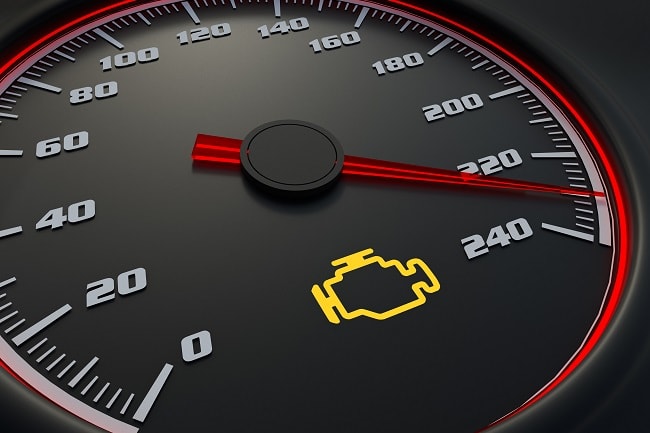

This one is a clear symptom that something is wrong. Though not the only reason why the check engine dashboard light may come on, if an ignition coil is faulty and not operating as it should, the ECU will recognise this and set off the Check Engine light. The computer may have detected that there is a coil that has burned or shorted out and needs replacing. If this happens, it is best to take the car to a garage to have the ECU scanned and check the code to see if a faulty ignition coil is the culprit.
3. Car is not starting
A problem that surely won’t take you long to notice! This could really be down to a spark plug, the distributor, or a number of other factors, but a faulty ignition coil can also lead to a vehicle not starting. For cars that use a single ignition coil as the source of spark for all of the cylinders, a faulty coil will affect the operation of the entire engine. If the coil fails completely, it means there will be no spark and therefore no engine.
For things like ignition coils, it is best to get them checked out at a garage to be sure that is the problem. While spark plugs can be replaced relatively easily, coils are a little harder to repair or replace, so it is best to leave them to professionals.
How can I test my ignition coils to see if they are the problem?
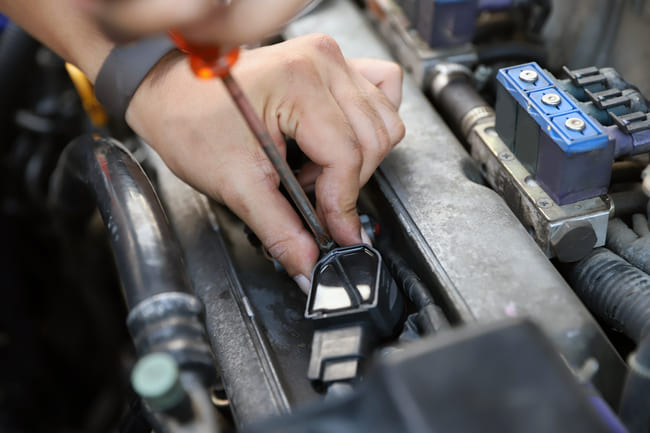

If your car has a distributor-based ignition system, all the spark plugs will be affected but if it’s a modern car with electronic ignition, only one plug could be, or two if they share the same coil. This can make it tricky to work out what the problem is.
Luckily, for cars built after 1996, they will have an OBD II (on-board diagnostic) port with misfire detection, and you can interrogate it using a diagnostic tool, check for the code P030X, X being the number of the cylinder that is faulty. This will let you know if the ignition coil is the problem or not.
Of course, a faulty cylinder can be caused by all manner of ignition and fuel supply problems, not just a faulty coil. For this reason, you should remove and check the spark plug, and, if there is a distributor, the HT lead.
Check the security and integrity of the coil itself. Also, you can perform an ignition coil ohm test using a multimeter, and this will check the coil’s primary and secondary resistance are to specification. This will be given in your car’s user manual.


















Comment