
AMT is an automated manual transmission. Structurally it is based on a manual transmission, however, differs from the latter by presence of the automatic gears and clutch control system.
Advantages of the AMT are:- comfort of operation;
- efficient energy consumption;
- reliability;
- relatively low cost, in comparison with the classic automatic transmission.
The AMT can operate in automatic and semi-automatic modes. In the latter, the driver changes gears sequentially using the console shift lever or paddle shifters.
In automatic mode control of the AMT is performed by the electronic system, components of which are:
The control unit analyzes input information, particularly, readings of oil temperature and pressure, positions of the gear lever and shift fork. Based on the analysis data, it sends commands to the actuation mechanisms.
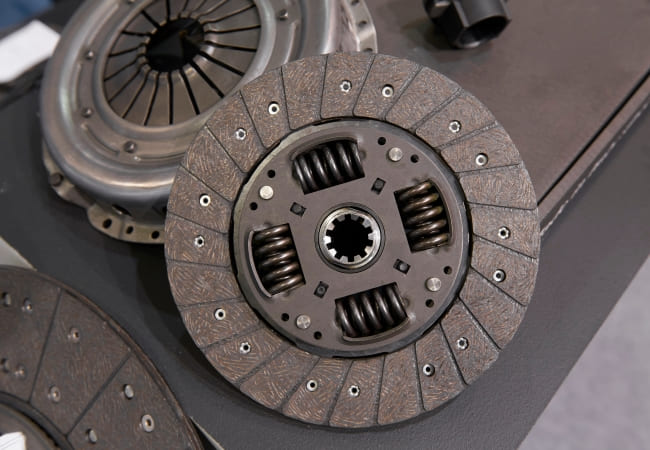
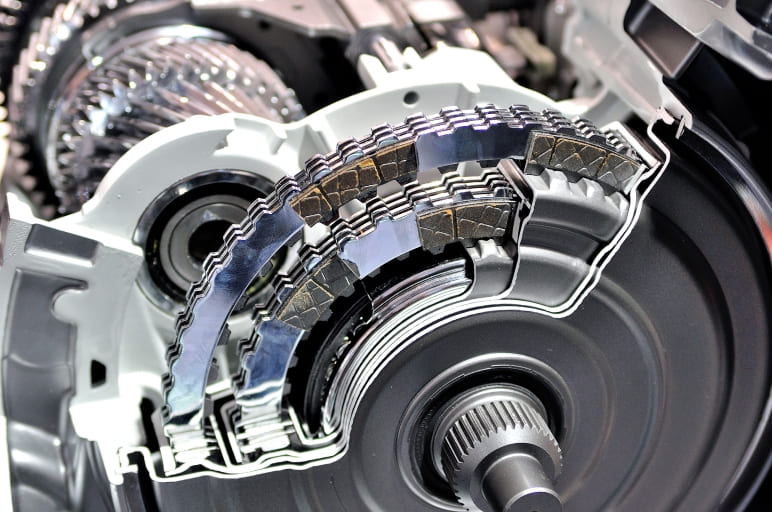
The AMT is equipped with the friction-type clutch. Modern cars can have the dual-clutch gearbox. The latter transmits rotating torque from the engine, without breaking powerflow.
- DCT M Drivelogic (BMW);
- PDK (Porsche);
- DSG (Volkswagen);
- Speedshift DCT (Mercedes-Benz);
- Powershift (Ford, Volvo);
- S-Tronic (Audi);
- Twin Clutch SST (Mitsubishi);
- TCT (Alfa Romeo).
- With electric drive.
- Allshift (Mitsubishi);
- Durashift EST (Ford);
- Dualogic (Fiat);
- MultiMode (Toyota);
- Easytronic (Opel);
- 2-Tronic (Peugeot);
- SensoDrive (Citroën).
- With hydraulic drive.
- SMG (BMW);
- Selespeed (Alfa Romeo);
- R-Tronic (Audi);
- Quickshift (Renault);
- ISR (Lamborghini).
The actuation mechanisms of the AMT with electric drive are electric motors; while those of the hydraulic drive AMT are hydraulic cylinders, controlled by electromagnetic valves. The control system of the hydraulic drive AMT includes the hydraulic control unit, which controls operation of the hydraulic cylinders and maintains pressure in the system.
The hydraulic drive, in comparison with the electric one, is characterized by higher energy demands: additional energy is consumed for maintaining the system pressure. The advantage of the hydraulic drive over the electric lies in high speed of operation.






Comment