
SRS (Supplemental Restraint System) is a system of passive safety which aim is protecting the driver and passengers in case of emergency situation.
SRS elements include:- front and side airbags;
- active headrests;
- seatbelts pretensioners;
- sensors;
- control module.
SRS components can be located in different parts of the vehicle – under the bonnet, in the seats, and also on the centre console.
The SRS sensors aim is to measure parameters of car movement and follow position of people in the passenger compartment. This information is sent to the control module which gives a command to operational units.
In case of emergency, for example, when a car collides with an obstacle while driving at a speed of 50 km/h and faster, inertia sensors are activated. As a result, the module activates propellant charges of airbags. As a consequence, airbags deploy.
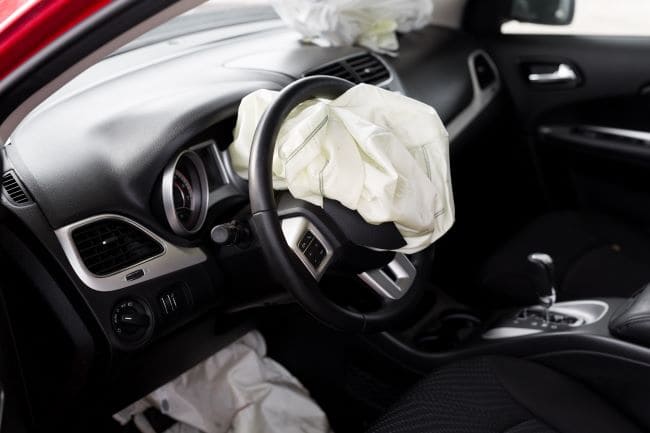

Airbags inflation is performed with the help of dry gas which is contained in capsules: under the influence of electric impulse the latter are melting, gas is released and fills the airbag.

- the car rams into a soft object;
- impact comes from the back (active headrests activate);
- impact comes from the side, and side airbags are not provided.
Separate sensors follow if a person fastened or not. Seat belts tension degree can increase after receiving the appropriate signal from the SRS module.
The SRS system interacts with the central lock: the doors, which were locked at the moment of accident, are unlocked after the signal from SRS. It gives rescuers access to injured people.

















Comment