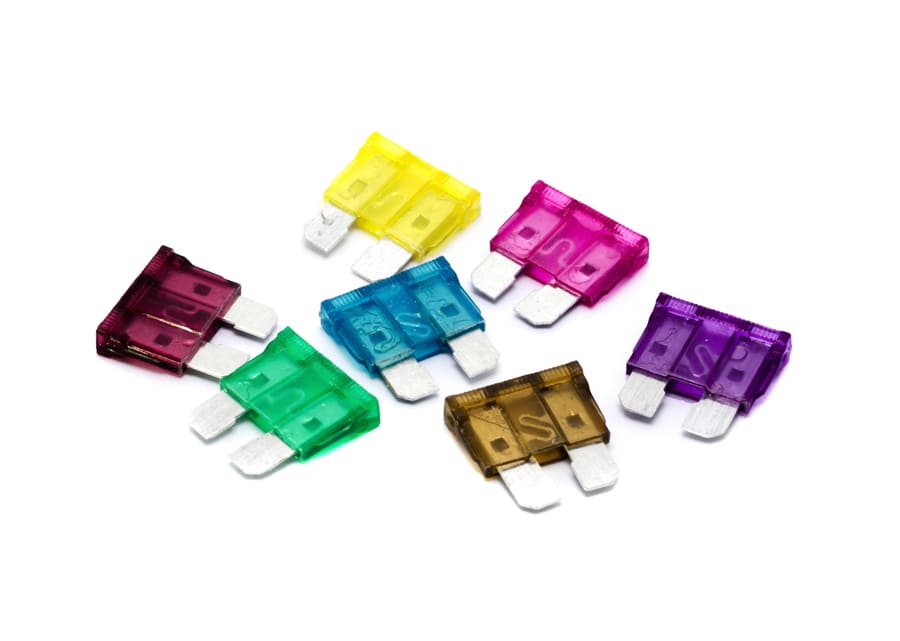

There is a large variety of car fuses. They are needed to protect motor vehicle circuits. In the earliest automotive days, cars did not have fuses. However, as vehicles have become more complex, the need for them has increased.
3 Main types of car fuses – blade, torpedo, and glass tube

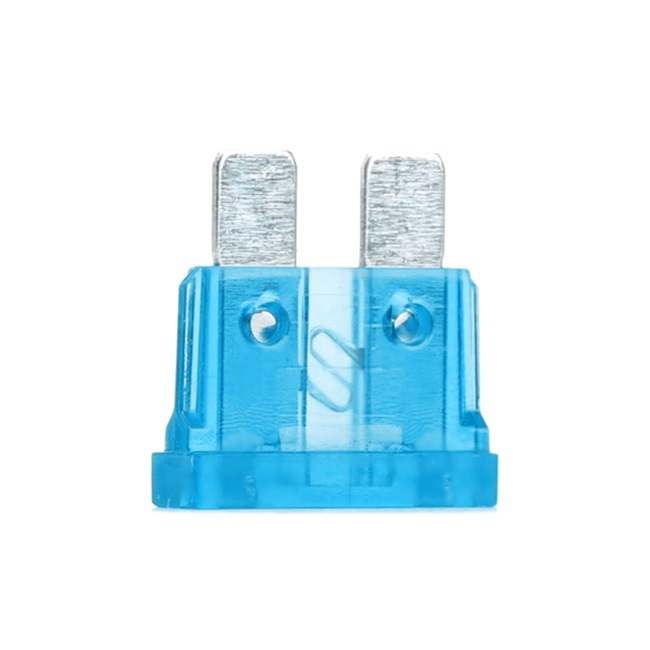
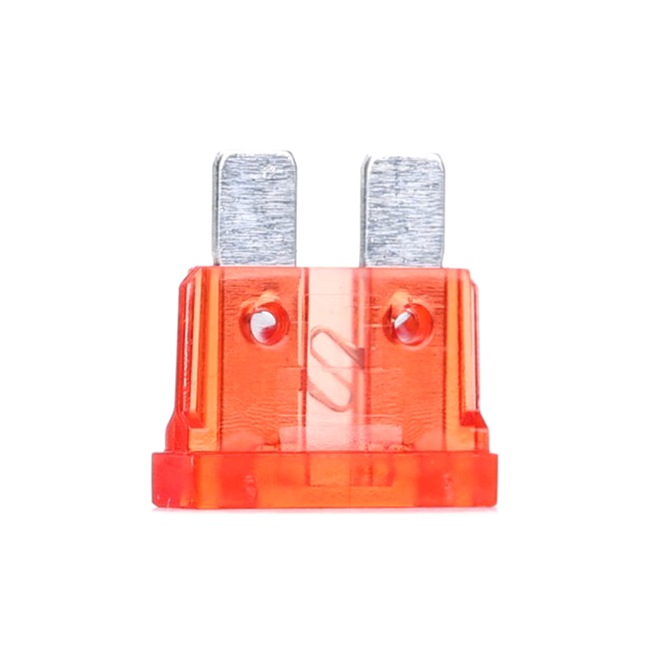
Blade – the standard for automotive circuit breakers They are made of see-through material and make it easier to quickly identify if it has blown. Every modern one for cars and motorbikes has the amperage number printed on the top. If it is older, the imprint is often illegible, in this case, you can still find out the amperage, because this this is coded by the colour of the transparent plastic casing that surrounds the metal strip. For example, black is 1A, red is 10A, and orange is 40A. The more amps the fuse has, the more current it can withstand before it blows.
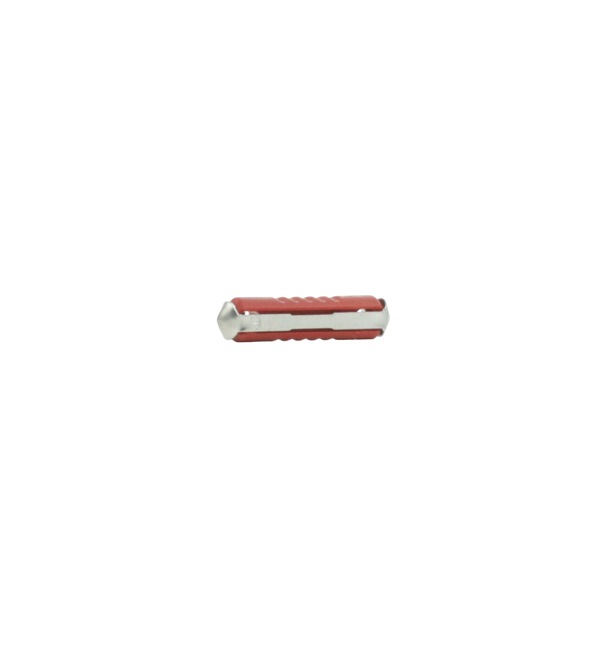
Torpedo – can be found in older European models and are differently designed than a blade fuse. They are easily recognised because of their “torpedo shaped” plastic casing. Just like the blade fuse, it is an overcurrent protection device that breaks the circuit by overloading when the current exceeds a certain value.
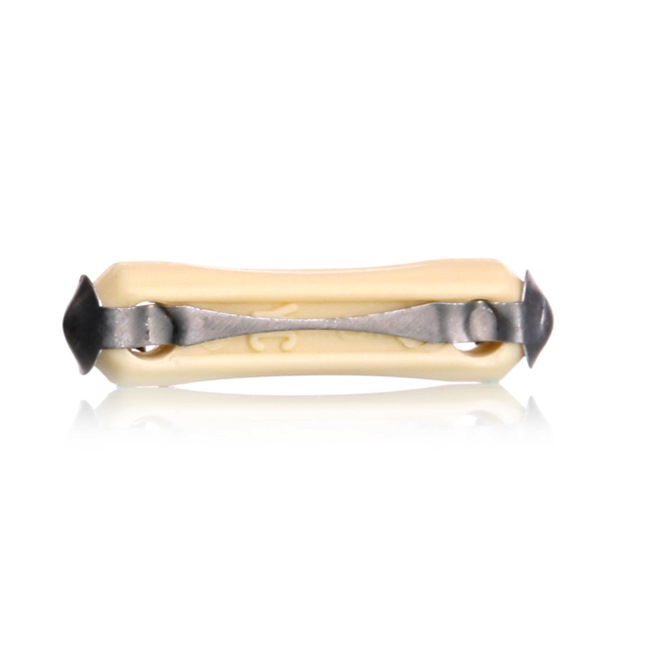
Glass tube – before the invention of the blade-type fuses, these were the main ones found in cars. They are made of two metal end caps terminals with a wire element. This wire is connected to the end caps and gives the direction for the electrical current. They are now quite rarely found in cars.

The fuse box
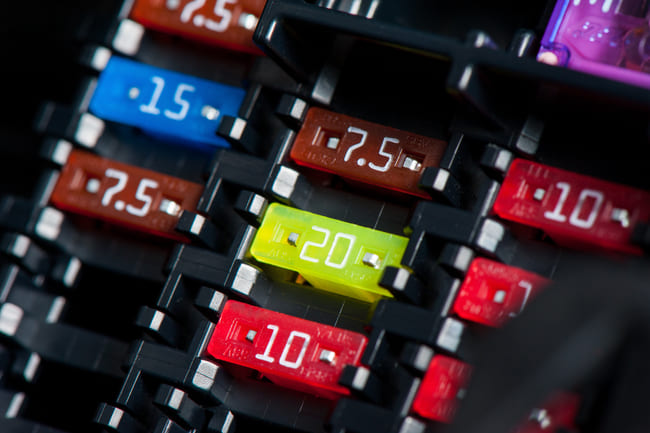

First of all, it is necessary to find out where it is located in the car. In most cases, a simple look in the manual will help. Popular places to put the fuse box are the engine compartment, the side end of the dashboard or the space under the driver or passenger seat.
The car’s fuse box contains the fuses, and it also often houses the electrical relays. Although it is usually made of durable plastic, it can wear out over time or become damaged due to various causes, such as a short circuit, or if it has become wet. If there are signs that it is defective, it must be replaced, whereby expert car mechanics are happy to change the fuse box themselves.
How to check if your fuse is blown
If you notice that there are some minor electricity issues, such as your interior lights aren’t working, or your air conditioning isn’t working correctly – it’s time to check your fuses.
Firstly, you should always disconnect the power supply in the car by disconnecting the power cables from the battery. The location of the battery can also be found in the manual; it is usually located in the engine compartment or in the rear of the vehicle. After disconnecting the battery, it may be necessary to re-enter the code to unlock the radio, so keep this code handy. This can also be found in the manual that comes with the vehicle. If you don’t have your manual at the ready, you can find the code on smartphone apps, or internet sites.
Now that you have opened the fuse box, you can first carry out a visual check of the car fuses. Since these are usually made of transparent plastic, it is possible to find out if one has blown without opening it.
If the visual inspection does not reveal any specific problems, the next step is to find out the configuration of the fuses. You will find a chart with the layout either in the vehicle manual or on the cover of the box.
Now remove the one that is responsible for the electrical failure – for example, if the electric windows have stopped working, remove the fuse for the electric windows accordingly. To check the car fuse, pull it out and hold it toward the light. If you notice that the metal strip in the middle is broken, you have a blown fuse.
Checking with a Multimeter
A multimeter is a measuring instrument that measures electrical current, voltage and resistance. Here are the steps for using it.
Caution
Never replace a blown or possibly damaged fuse with one with a higher voltage. They have this number for safety reasons and you should always replace a fuse with the exact same (or sometimes lower) value as the old one.

















Comment