
The modern car with an internal combustion engine is fitted with a turbocharger or even a supercharger. These are intended to improve fuel efficiency and performance in standard petrol or diesel-fuelled cars. With the advent of modern technology, the car industry is beginning to introduce electric turbos. But what are these strange new devices? Read on and find out what ingenious bit of tech is hiding behind that name.
What is a conventional turbocharger?
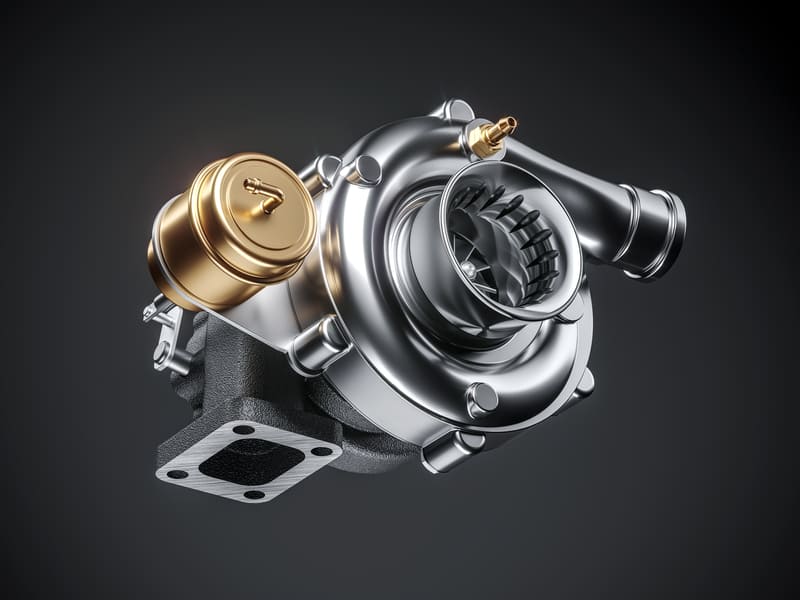
The bog-standard turbocharger, or turbo, is a device that increases the output of an internal combustion engine through the forced induction of compressed air. Since an internal combustion engine generates locomotion by burning a fuel-air mixture, the rate at which this mixture is burned is a major factor in determining the engine’s power output. A faster burn rate results a more powerful operation. To achieve this, the turbo is powered with hot exhaust gases. This results in a spinning of a turbine that compresses air that is eventually delivered to the engine.
A supercharger works the same way, but the method by which it is powered is dissimilar. While a turbo is powered by hot exhaust gases, the supercharger is driven directly by the engine. This results in distinct advantages and disadvantages of the two variants: turbochargers take a while to get going, since they rely on exhaust gases to function, while superchargers are less fuel-efficient but increase engine power from the moment the engine turns on. This tendency of turbos to take time before becoming fully functional is referred to as turbo lag.

What is an electric turbocharger?
An electric turbo attempts to offer the best of both worlds: the brutal efficiency of a fully active turbocharger coupled with the elimination of the pesky turbo lag that a supercharger brings to the table. It should come as no surprise that their basic functionality is essentially identical to that of a standard turbo: Much like its non-electric counterpart, the E-turbo is powered by hot exhaust gases generated by the engine while the vehicle is being driven. Unlike the conventional turbo, however, it also includes either a small air compressor which in turn is powered by an electric motor or an electric motor to turn the turbines when there isn’t enough exhaust gas available. This provides the compressed air required to boost engine power before the traditional turbocharger is warmed up and functional. As soon as the exhaust-powered turbo is fully operational, the electric motor shuts down to avoid unnecessary drain on the car battery.
Advantages of electric turbochargers
The advantages of an E-turbo are plainly visible: it eliminates turbo lag by providing the air input normally supplied by a turbocharger once it is warmed up. Unlike a supercharger, electric turbos aren’t active the whole time and thus don’t reduce engine power at all while providing the same level of torque throughout regardless of the engines rpm. While the power increase gained from using a supercharger outweighs the cost in engine power to keep it running, an electric turbocharger can skip sapping engine power to remain active in the first place, thus increasing the power gained from activating the device. They also have the advantage that they can be switched off when not needed, such as when driving long distances at a constant speed. This allows the engine to function at a higher efficiency and saves fuel in the long run. Now, it can be said that the benefits of an electric turbo can be achieved just as well with a twincharging system, that is a combination of turbo- and supercharger. While this may be the case, an E-turbo takes up significantly less space and achieves the effect of the supercharger part of the system without power loss. Electric turbos also reduce emissions overall and have the potential of using exhaust gases to power generators when these are not needed.
Disadvantages of electric turbochargers
Electric turbos are still very new and thus not all of the kinks have been ironed out of this advanced technology. For one, the electric turbo still aims to increase a vehicle’s performance. A reduction in fuel consumption or emissions isn’t its primary purpose, so it will likely cause an increase to both, even if not as much as with a conventional turbo- or supercharger. Furthermore, given its status as emerging technology, electric turbocharging will remain comparatively expensive for some time. Its reliability is also largely untested, given the lack of data, which in turn is a result of the limited application. It can also be said that electric turbochargers are increasingly unnecessary given how the writing is on the wall for fossil fuels and thus internal combustion engines that use petrol or diesel. With the increased availability of electric cars, turbochargers may become a thing of the past entirely.
Installing an electric turbocharger
If you are wondering how to install an electric turbocharger, you need to beware of the nature of many private offers online. In many cases, these electric turbos are little more than fans that provide little to no extra power. Rely on trusted manufacturers instead and opt for having these devices installed by experts in a garage sufficiently equipped to service this sort of technology. If you do intend to install the device on your own, make sure you have the necessary experience and read the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to avoid any errors.
- @user_286884529.08.2024 20:34Member
can an electric turbocharger be installed independently of the cars exhaust manifold system?
 @Graziana Venturi04.09.2024 14:43Moderator
@Graziana Venturi04.09.2024 14:43ModeratorGood evening! It is not possible to provide a definitive answer, unfortunately. To obtain an accurate assessment, it is necessary for specialists at the garage that installed the system to inspect your car's engine and intake system.
















Comments – 2